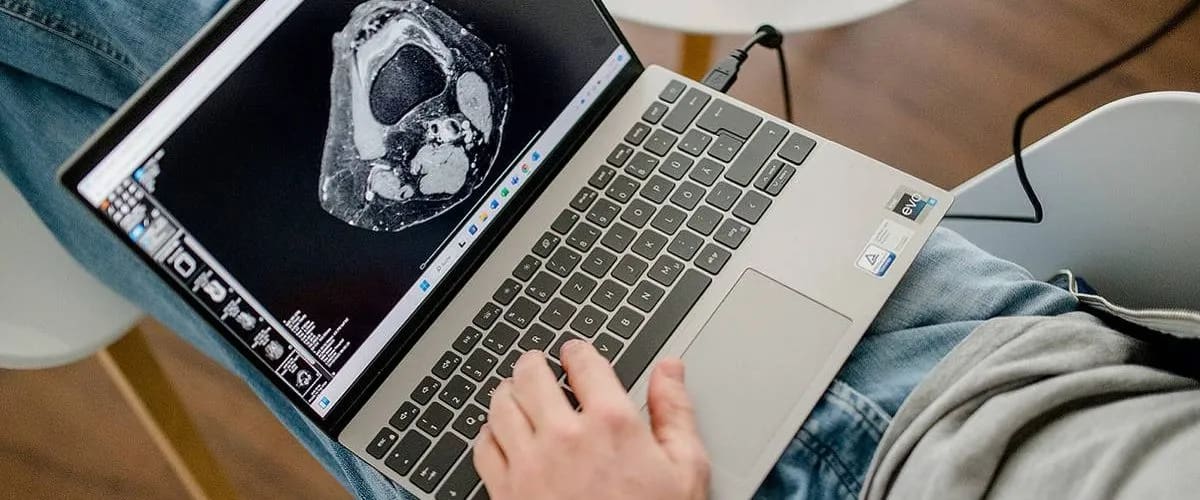
Picture archiving and communication systems, short: PACS, play a vital role in diagnostic medicine as they replaced conventional ways of handling and storing images with digital image-viewing. Should a PACS be installed on-site or be accessible remotely? Cloud PACS versus on-premise PACS—a long-led discussion we also want to pick up today.
📖 Author: Emmanuel Anyanwu | Alberta Health Services, Canada
The advent of picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) has transformed the medical imaging world by replacing the conventional ways of producing images with digital image-viewing. This imaging technology used to securely store, retrieve, and digitally transmit electronic images (X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs) and patient data has made the radiology department more efficient and productive. Besides eliminating the conventional ways of storing images, PACS allows radiologists, referring physicians, and radiographers to instantly access patients’ medical images and reports from any location. This results in expedited diagnosis accuracy and the development of treatment plans.
Some factors in medical imaging vital to patients’ health and care include speed, cost-effectiveness, accuracy, and security. These factors, amongst others, are considered by decision-makers when deciding what kind of PACS solution, whether cloud-based or on-premise, best suits their healthcare facility.
Cloud PACS
Cloud-based PACS is hosted on remote servers and accessed through the internet. Medical images in a cloud PACS are stored in a secure data center operated by a third-party vendor rather than on the hospital’s server. Cloud PACS allows healthcare providers to access these images from any location with an internet connection using a web-based interface or specialised software like an HTML5-compatible device. They can view these images or data on most devices, including mobile devices and tablets.
A senior analyst at Signify Research, Amy Thompson, says, “One trend that we cannot deny and it keeps growing each year is cloud, especially in radiology IT. It has been a buzz term for a couple of years. We started to see an emphasis at RSNA 2020 on cloud PACS and cloud imaging IT. But we are really starting to see the vendors and the market become more accepting of it.”
Advantages of cloud PACS
- Accessibility: With Cloud PACS, healthcare providers can access medical images from anywhere and anytime as long as they have an internet connection. This primarily works when telemedicine and remote consultations are needed (weekend and late-night shifts), thus saving the radiologists time to travel from one location to another. Easy access to patient images and information results in faster diagnosis and treatment plans.
- Scalability: Cloud PACS can quickly scale up or down based on the healthcare provider’s needs—number of users, storage requirements, and processing power needed. This could be advantageous for smaller healthcare providers who may not have the resources to set up and maintain their own on-premise PACS system.
- Cost: The cost-effectiveness of Cloud PACS is very beneficial for healthcare providers because it saves them money in investing in expensive hardware and software for an on-premise PACS system. Additionally, cloud PACS vendors are responsible for system maintenance and upgrades, which can further reduce costs for healthcare providers.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud PACS are often backed up and archived in case there is some damage to the primary data storage. This way, the healthcare providers wouldn’t experience any delay in accessing patient data and information because of the availability of backed-up secondary data.
Cloud PACS challenges
- Security: The security of stored medical images and patient data in the cloud is always a concern for healthcare providers because of data security and privacy. There is always the risk of data breaches. Hence, healthcare providers must carefully vet cloud PACS vendors to ensure they comply with industry data security and privacy standards.
- Reliance on internet connection: A stable internet connection is required if cloud PACS is to operate effectively. Healthcare providers may experience delays accessing medical images if the connection is slow or unreliable.
- Data ownership: With cloud PACS, healthcare providers do not own the system’s physical infrastructure and must rely on the vendor to maintain the system. This may concern some healthcare providers who prefer more control over their patient data and infrastructure rather than storing them on servers owned by a third party.
On-premise PACS
On-premise PACS are hosted on the healthcare provider’s server and accessed through the hospital’s network. In an on-premise PACS, medical images are stored on the hospital’s servers, and healthcare providers can access these images using specialised software installed on their local computers.
Advantages of on-premise PACS
- Control: Unlike Cloud PACS, healthcare providers have complete control over their data and infrastructure with on-premise PACS. This means they can customise the system to meet their needs and have complete control over data security and privacy.
- Security: On-premise PACS allows for direct control over data security. The data is stored on the hospital’s servers and not transmitted over the internet. Healthcare providers can implement their security protocols and control access to the system more tightly.
- Reliability: With on-premise PACS, healthcare providers do not have to worry about internet connectivity issues or outages, outside of their facility, that could disrupt access to medical images. The system operates entirely on the hospital’s network, which can provide excellent reliability.
Disadvantages of on-premise PACS
- Upfront costs: Setting up and maintaining an on-premise PACS system can be expensive—requiring significant investment in hardware, software, and IT personnel.
- Scalability: Scaling up an on-premise PACS system can also be costly and time-consuming because it would require additional hardware and software to be purchased and configured.
- Maintenance: Healthcare providers are responsible for maintaining and upgrading the on-premise PACS system, which can be time-consuming and require specialised IT expertise.
With the advantages and disadvantages of both cloud PACS and on-site PACS mentioned above, it is evident that they are both beneficial to the hospital or imaging center, depending on the specific needs, budget, and security concerns of the healthcare providers. Cloud PACS may be a better option for facilities with limited IT resources—and it is definitely trending and playing the sound of future.
—
What kind of PACS do you prefer to work with? Share your thoughts via the comment section below.
Want to join a great team? Check out our careers section. We are always looking for outstanding talent—from application specialist to software developers.
📷 Photo credits: daniela-mueller.com