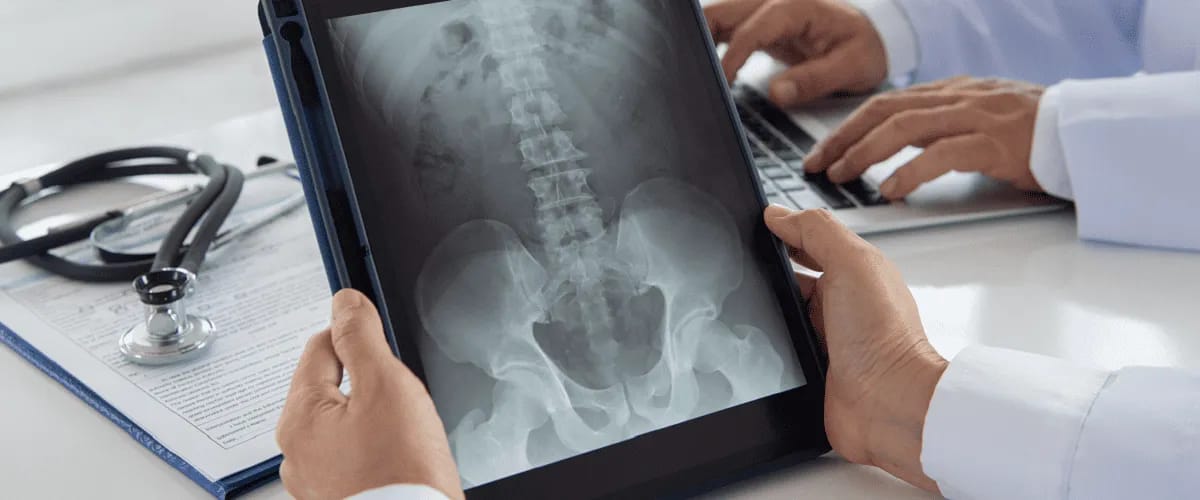
Radiography (also called X-ray) is a commonly used examination to identify many medical conditions. This article aims to give the reader a deeper understanding of radiography. It explores the basics of radiography, including its advantages and disadvantages.
It is important for healthcare professionals, or those considering a career in healthcare, to understand what radiography is and how it works. This imaging technique is essential in the diagnosis, management and monitoring of many medical conditions.
Radiography explained
Radiography is a medical technique that uses ionising radiation to view internal parts of the body. It is a diagnostic imaging technique in which an X-ray beam passes through the body and signals the presence of foreign bodies, damage to a body structure, signs of organ dysfunction and other abnormalities.
During an x-ray the tissues being examined absorb radiation to different degrees—resulting in a contrast of black and white which allows the internal anatomy to be seen. The radiation is not felt by the patient and does not cause any discomfort.
X-ray imaging is a versatile diagnostic tool that enables the examination of various body structures—including bones, joints, and soft tissues. This imaging technique is capable of detecting a wide range of health issues such as bone fractures, lung diseases, scoliosis, digestive problems, and both cancerous and non-cancerous tumors.
In some cases, because a clearer image of the structure being visualised is needed, a contrast agent is used which is administered to the patient in different ways: orally, by injection or by insertion into the rectum.
Procedure step by step
X-rays may be taken in the radiology department of a hospital, in a clinic or medical facility where various diagnostic procedures are performed. X-rays are done by trained radiology technicians who are responsible for operating the equipment and taking the images which are then interpreted by a radiologist.
These are the main steps of the procedure:
- The technician gives the patient instructions on the position to take during the examination. Depending on the type of X-ray the patient may lie on a table, sit or stand . They may also need to wear a hospital gown and remove any jewellery.
- The X-ray machine is aimed at the part of the body to be examined.
- The images are taken by a detector and sent to a computer for processing. The patient is asked not to move so that the images are clear.
- The test is completed when the images are clear enough. They are then interpreted by a radiologist who will look for any abnormalities (infection, tumor, fracture, etc.).
Pros of an X-ray
X-ray imaging exams have several benefits:
- They are non-invasive and painless.
- The procedure is quick and convenient.
- They are a versatile diagnostic tool.
- They are cost-effective.
- Modalities are small (in comparison to MRI or CT) and can be kept in smaller surgeries.
- X-rays exams detect a wide range of diseases.
- X-rays provide valuable information for developing an effective treatment plan and monitoring a disease.
Cons of radiography
X-rays are an effective diagnostic tool but there are also some risks associated with them that need to be mentioned. In general, the dose of radiation used in an X-ray is safe for an adult but not for a baby—so the radiographer should be informed if the patient is pregnant.
In the long term repeated exposure to radiation can have harmful effects but generally the risk from X-rays is considered to be very low. During the examination the patient is exposed to an amount of radiation equivalent to the amount of natural radiation to which they would be exposed in a few days to years (depending on the type of X-ray).
People are exposed to ionising radiation from the environment every day and repeated X-rays can increase the risk of developing cancer later in life—but this type of imaging uses a small amount of radiation compared to other imaging tests available today.
Applications of radiography in healthcare
In the medical field X-rays have a wide range of applications and are crucial in the detection of many diseases. Here are a few examples:
- The dentist recommends that patients have X-rays taken before starting dental treatment as the images can help detect early-stage decay and infections that are not visible to the naked eye.
- Lung, breast and colon cancer are cancers that can be detected by X-rays.
- Specialists can use X-rays to quickly detect lung problems such as pneumonia, bronchitis and other lung diseases.
- As well as detecting many diseases, X-rays are useful for monitoring the effectiveness of treatments and the development of a tumor.
Best practices in radiography
The radiographer is responsible for operating the equipment and using the technology appropriately. They should consider the needs of the patient and provide a comfortable environment.
Radiographers must follow safety protocols to minimise the risk of overexposure to ionising radiation. One of the ways they fulfil this requirement is by providing the patient with protective equipment such as lead aprons. Other precautions include the removal of metal objects and jewellery by the patient, which the radiographer is responsible for informing the patient about.
For the images obtained to be useful for diagnosis, they must be of high quality. The quality of the images depends on the quality of the equipment but also on the correct positioning of the patient and the choice of appropriate exposure parameters. Another example of good practice is an interest in the latest technology. This sometimes depends on the clinics and their willingness to upgrade their equipment and make major investments in the latest technology.
All in all, radiography is an important non-invasive imaging technique used to detect a wide range of medical conditions in the bone, lungs, teeth and beyond. It is likely that the future of X-ray technology will continue to see advances and improvements so that the risks, which are already very low, will become even lower.