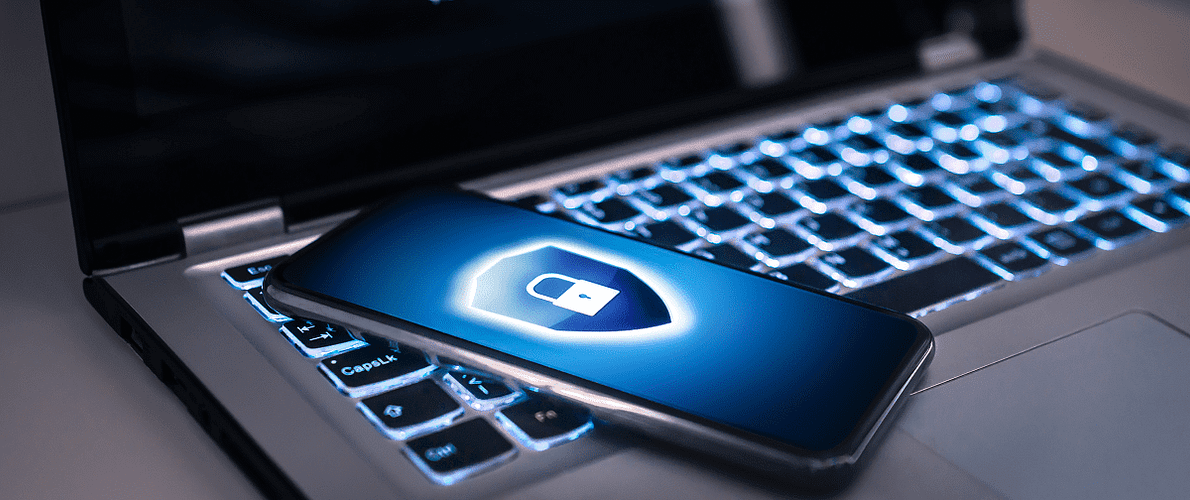
Radiology has ingrained itself as a critical aspect of modern medicine. But with the huge increase in digital imaging and information systems, radiology cybersecurity has become a concern because of the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches. Learn more about cybersecurity in radiology and how you can raise security.
📖 Author: Emmanuel Anyanwu | Alberta Health Services, Canada
According to the consulting company Gartner, “Cybersecurity is the practice of deploying people, policies, processes and technologies to protect organisations, their critical systems and sensitive information from digital attacks.” This also counts for radiology and all companies and institutions acting in that medical field.
The need for radiology cybersecurity
With imaging technologies playing a key role in diagnosing and treating many conditions, radiology has ingrained itself as a critical aspect of modern medicine. The constant insight that the medical imaging world provides makes it one of the most valuable innovations in the healthcare industry. However, with the increase in digital imaging and information systems, radiology cybersecurity has become a concern because of the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches.
To ensure the security and privacy of sensitive medical information, it is essential for radiology departments to implement strong cybersecurity measures. According to the American College of Radiology, $9.23 million was the average healthcare data breach cost in 2021. The cost of global cybercrimes in 2025 is expected to rise to $10.5 trillion. Considering this, the need for radiology cybersecurity has never been more urgent and essential.
Radiology as a target for cyber-attacks
Radiology departments hold a vast amount of valuable data associated with medical imaging alongside personal and medical information of patients, names, addresses, social security numbers, medical histories, and diagnostic images. Hackers and cybercriminals find all this information highly valuable because they can use it for identity theft, insurance fraud, or sell it on the dark web.
Another critical fact is that, more often than not, the radiology systems are integrated into a hospital’s more extensive network, making the radiology department a potential earmark in the organisation’s overall security. Hackers may use this vulnerability to access the hospital’s systems, steal sensitive data, or install malware to compromise the network.
According to Po-Hao Chen, MD, MBA, chief informatics officer of imaging, IT medical director, and musculoskeletal radiologist at Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, “Hospitals have to be operational at all times. You cannot take a hospital computer system down to upgrade it or patch a security hole. For that reason, they are easy targets.”
Risks of a data breach in radiology
Many people find patient data to be vital. Unfortunately, this goes for both legal and illegal entities. In the wrong hands, this data can be considered a security breach and could endanger patient confidentiality and jeopardise trust in a hospital or imaging centre. A data breach in radiology can result in severe consequences for patients and hospitals or imaging centres whose data has been compromised. Some of the risks include the following:
- Patients risk identity theft and financial fraud if a breach exposes their sensitive personal and medical information.
- A lack of information security can lead to a data breach, damage a hospital’s or imaging centre’s reputation, and undermine public trust in the organisation.
- There can be substantial financial consequences where a data breach results in legal action against the hospital or imaging centre.
- Healthcare facilities stand to lose business once patients feel their privacy is not sufficiently protected. They may seek care in another place where they are guaranteed data protection.
Steps to improve radiology cybersecurity
There are several ways hospitals and imaging centres can boost their radiology cybersecurity and be protected against data breaches:
- Be proactive: The hospital’s or imaging centre’s IT systems should integrate adequate controls and measures into all aspects of its operations—including technical, operational, and management tiers. This prevents, at best, or minimises the risk of cyber-attacks.
- Educate staff: Employees should be trained on the importance of cybersecurity best practices—strong password management, updating software regularly, data encryption, etc. The team who handles security protocols should also have an Incident Response Plan in place, just in case the organisation falls victim.
- Security assessment: Every healthcare organisation or imaging centre should regularly conduct security assessments to monitor risks and catch any impending threat before something happens. This way, they can reduce any vulnerabilities in any device or connection. Firewalls and anti-virus software can also help to prevent unauthorised access to radiology systems and protect against malware.
- Partner with trusted vendor: Partnering with a trusted radiology company, like OpenRad that provides excellent solutions that improve service delivery to patients and ensure health information, is secure and not vulnerable to unauthorised access.
All in all, cybersecurity is a critical issue for radiology practice and must be taken seriously to protect sensitive medical information and maintain patients’ trust. By improving cybersecurity and implementing best practices, radiology departments can reduce the risk of a data breach and protect sensitive information.
—
Is there anything to add from your side to increase radiology cybersecurity? Share your thoughts via the comment section below.
Want to join a great team? Check out our careers section. We are always looking for oustanding talent—from application specialist to software developers.