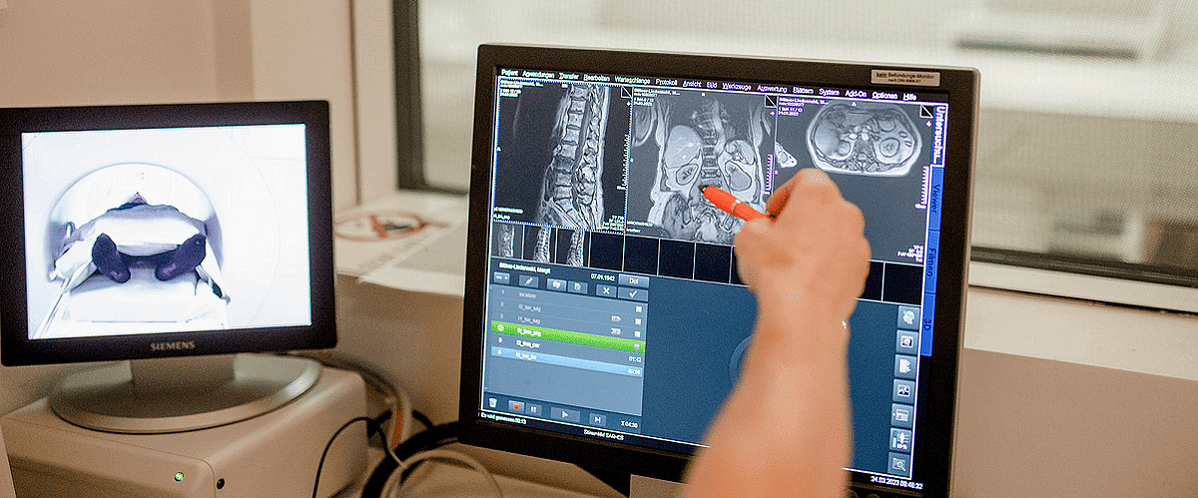
This month’s radiology trends picks look into medical technology advancements and their potential to improve diagnostics, treatment, and patient outcomes in healthcare. Explore innovative techniques such as correlated diffusion imaging (CDI) for studying COVID-19’s impact on the brain or the integration of 5G technology in healthcare.
📖 Author: Sandra Dietrich | OpenRad team
New MRI technique reveals COVID-19’s brain impact
According to itn, a new MRI technique called correlated diffusion imaging (CDI)—developed by a Canadian engineer at the University of Waterloo—has been used to study the impact of COVID-19 on the human brain.
The study, conducted by scientists at Baycrest’s Rotman Research Institute and Sunnybrook Hospital in Toronto, revealed that COVID-19 can cause changes in the white matter of the brain.
CDI was able to identify diffusion abnormalities in different regions of the brain affected by the virus. The research highlights the potential of CDI not only for COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment but also for understanding other diseases and detecting cancers.
Radiology Trends: 5G Medical technology advancements
According to Health Tech World, the healthcare industry is undergoing a transformative phase—driven by medical technology advancements. The integration of 5G technology is revolutionising healthcare by enabling faster and more reliable data transfer, facilitating real-time communication, and supporting innovative applications.
With the potential to enhance telemedicine, remote monitoring, robotic surgery, and augmented reality interventions, 5G offers personalised and preventive healthcare experiences.
While healthcare organisations need to carefully evaluate the implementation of 5G and address cybersecurity and privacy concerns, the benefits of this technology are substantial and can lead to improved patient outcomes, reduced costs, and increased operational efficiency.
AI tool to detect splenomegaly on CT scans
A recently accepted manuscript in the American Journal of Roentgenology highlights the potential of using an automated deep-learning AI tool and weight-based volumetric thresholds for large-scale evaluation of splenomegaly on CT scans.
Traditional linear measurements of the spleen have been suboptimal in detecting volume-based splenomegaly. The study, led by Dr Perry J. Pickhardt, utilised a deep learning algorithm to calculate splenic volumes in a sample of over 8,900 patients who underwent CT examinations.
The researchers found that weight-based volumetric thresholds were effective in indicating the presence of splenomegaly. This study represents one of the largest reported samples of patients undergoing volumetric segmentation of the spleen.
Brain imaging unveils obesity’s altered food response
According to itn, researchers have used molecular imaging to identify brain changes in response to food cues in individuals with obesity.
The study, presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2023 Annual Meeting, revealed that neuroreceptors in the brains of individuals with obesity respond differently to food cues compared to those of normal-weight individuals.
The findings offer valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of obesity and suggest that targeting these neuroreceptors could be a potential strategy for obesity interventions.
According to Osama Sabri from the Department of Nuclear Medicine at the University of Leipzig/Germany, the researchers hope that the study will lead to the development of new drug treatments and behavioural interventions to combat the global obesity epidemic.
—
Are there any radiology trends you would like to add here? Share your ideas or links to news articles via the comment section below.
Want to join a great team? Check out our careers section. We are always looking for exceptional talent—from application specialist to software developers.
📷 Photo credits: daniela-mueller.com