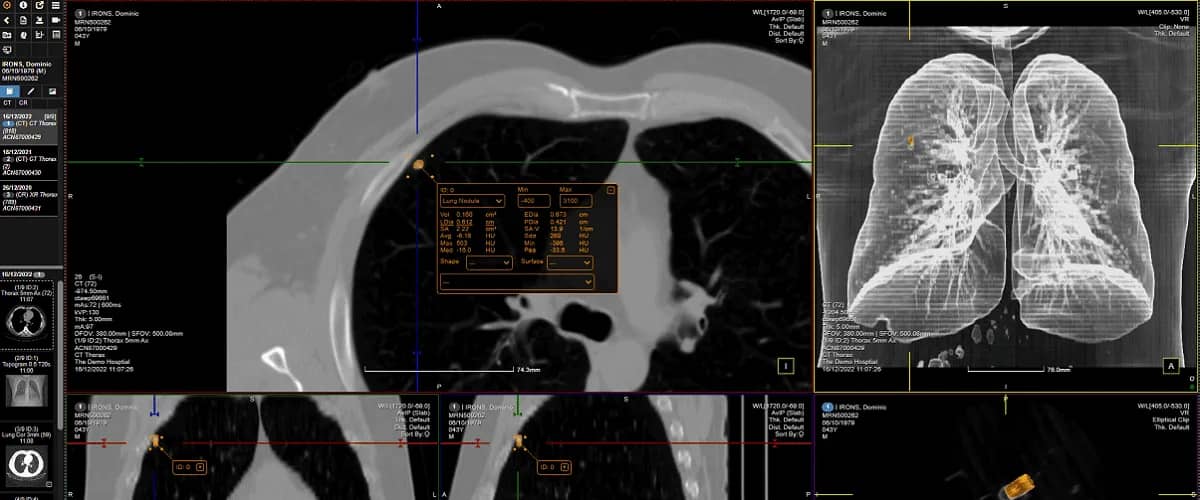
The Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine standard (short: DICOM) is a widely recognised and adopted format and protocol for managing and exchanging medical imaging data. Let’s explore more about it and how it works.
📖 Author: Emmanuel Anyanwu | Alberta Health Services, Canada
The Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine standard is an adopted format and protocol for managing and exchanging medical imaging data, including storing, transmitting, and sharing medical images and related information in healthcare settings.
It is fundamental in ensuring interoperability, standardisation, and seamless communication between medical imaging devices, software systems like Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), and healthcare institutions.
The introduction to the DICOM standard acknowledges its widespread usage in healthcare settings. DICOM-compliant devices and systems are employed in image acquisition, storage, retrieval, and viewing across hospitals, clinics, and research institutions globally.
The standard ensures that medical images can be accurately and reliably transmitted and accessed—enabling healthcare professionals to make informed diagnoses, develop treatment plans, and collaborate effectively.
How DICOM works
The Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine standard defines a set of rules and formats for organising and exchanging medical images and data. It encompasses various aspects, including image encoding, network communication, data structures, metadata, and security.
By standardising these processes, DICOM enables medical professionals to acquire, store, retrieve, view, and share images and associated data consistently and efficiently across diverse platforms and vendors—regardless of the equipment or software used.
It supports a wide range of medical imaging modalities such as X-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine, even endoscopy and echocardiograms, allowing for the exchange of two-dimensional and three-dimensional images. Additionally, DICOM facilitates the integration of other important information, such as patient demographics, clinical reports, annotations, and measurement data.
Usage
The Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine standard is utilised in various healthcare scenarios, including:
- Image acquisition: DICOM enables medical images to be acquired and stored in a standardised format directly from imaging devices, such as CT scanners or MRI machines.
- Image storage and management: DICOM-compliant PACS systems store, archive, and retrieve medical images, making them accessible to healthcare professionals across different departments or locations.
- Image sharing and interoperability: The Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine standard facilitates the exchange of medical images between healthcare providers, referrers, hospitals, and clinics, ensuring compatibility and seamless integration of imaging data.
- Viewing and analysis: DICOM-compatible software and workstations allow physicians and radiologists to view, interpret, analyse, and manipulate medical images effectively.
DICOM Protocol
The Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine standard employs a network communication protocol called the DICOM Application Layer Protocol. It uses TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) to facilitate the secure and reliable transmission of medical images and associated data over networks.
The DICOM protocol specifies the rules for establishing connections, negotiating capabilities, exchanging data, and managing error recovery during communication between DICOM devices.
Comparison of DICOM to other formats
Compared to older or proprietary formats, DICOM stands out as a widely adopted and comprehensive standard for medical imaging—ensuring interoperability among different vendors’ equipment and software. Older or proprietary formats lacked consistency and interoperability, which could hinder image exchange and collaboration.
The Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine standard promotes data integrity and patient safety by establishing a common language and framework for medical imaging data. It facilitates the seamless exchange of images and information, reducing the risk of miscommunication and errors.
Additionally, the standard continues to evolve and adapt to advancements in technology and imaging practices, ensuring its relevance and effectiveness in the ever-changing field of medical imaging.
Overall, the DICOM standard plays a vital role in the seamless integration, storage, sharing, and analysis of medical images, contributing to improved patient care, more efficient workflows, and enhanced collaboration among healthcare professionals.
—
Do you solely use DICOM at work or different formats? Share your experience via the comment section below.
Want to join a great team? Check out our careers section. We are always looking for outstanding talent—from application specialist to software developers.
📷 Photo credits: daniela-mueller.com