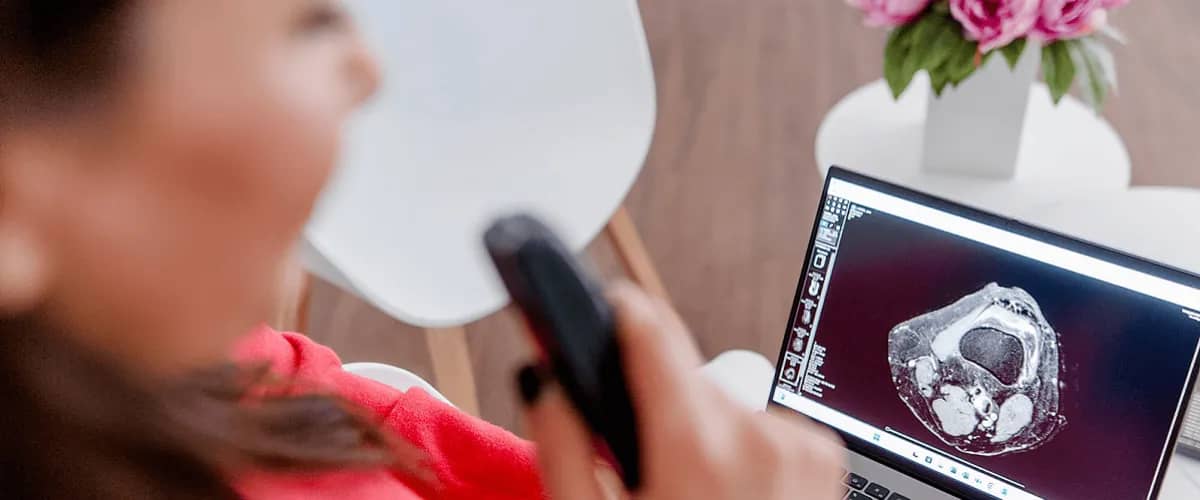
A radiology report is a written document that summarises the findings of a radiologist’s interpretation of medical imaging studies. Let’s explore how it is done and what it should contain.
📖 Author: Emmanuel Anyanwu | Alberta Health Services, Canada
A radiology report is a written document that summarises the findings of a radiologist’s interpretation of medical imaging studies—such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound, or nuclear medicine scans.
Although reporting style and format may vary between radiologists, the report is a crucial communication tool between radiologists, referring physicians, and other healthcare professionals involved in patient care. Thus, it needs to cover certain aspects and parametres known to and agreed by all involved parties.
Components of a radiology report
Radiology reports play a vital role in clinical decision-making and patient management. They aid referring physicians in making accurate diagnoses, determining appropriate treatment plans, and monitoring the effectiveness of interventions.
Moreover, the report is an official record of the radiologist’s interpretation, facilitating continuity of care, follow-up imaging studies, and medicolegal documentation. Here are some critical aspects of a radiology report:
Radiology report contents
A well-written and structured radiology report typically contains the following elements:
- Patient information: This includes the patient’s details like name, age, sex, and relevant medical history.
- Procedure: This describes the imaging procedure, the body part imaged, the imaging technique used, and any contrast agents or medications administered. It includes information about the technical aspects of the imaging procedure.
- Findings: This is a detailed description of the radiologist’s observations, abnormalities, and relevant measurements. In some cases, the radiologist may not give any information about a part of the body covered during the procedure because there was no relevant information to report to the healthcare provider.
- Comparison: This section may include comparisons with previous imaging studies (priors) that are relevant to the current exam, if available. Radiologists can get clearer insight and better understand the analysis and the patient’s medical condition with comparisons.
- Impressions or conclusions: This summarises the radiologist’s overall interpretation, diagnosis, or differential diagnosis. This section may also include recommendations for further imaging or additional diagnostic tests.
Report creation
Radiologists are doctors who specialise in interpreting diagnostic images. They generate radiology reports. They can identify and analyse abnormalities in imaging studies and provide expert opinions on the diagnostic implications.
Radiologists usually generate the radiology report based on their observations and findings from reviewing the images using specialised dictation software or with the help of a transcriptionist.
Radiology report audience
The primary audience for a radiology report is the referring physician or healthcare provider who ordered the imaging study. They rely on the radiologist’s report to assist in making accurate diagnoses, determining treatment plans, and monitoring the progress of a patient’s condition.
Other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care, such as surgeons, oncologists, or specialists from various medical disciplines, may also need access to the radiology report. This is why remote reporting and report access, as with OpenRad, is such a game changer in healthcare.
Report purpose
Radiology reports serve several purposes, including:
-
- Diagnosis: Radiologists provide detailed descriptions of abnormalities or normal findings to aid in diagnosing a patient’s condition.
- Treatment planning: The report helps healthcare professionals determine appropriate treatment options based on the radiologist’s findings.
- Communication: The report facilitates effective communication between radiologists and other physicians involved in the patient’s care, enabling collaboration and continuity of care.
- Documentation: The report is an official record of the radiologist’s interpretation, which can be used as a reference for future comparison or medicolegal purposes.
It is important to note that while the radiology report provides crucial information, it is just one part of the diagnostic process. The report should be considered alongside the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and other relevant clinical information to arrive at a comprehensive diagnosis and treatment plan. Effective collaboration and communication among healthcare professionals are essential for optimal patient care, with the radiology report serving as a critical component in this process.
—
What do you usually include in your radiology report? Share your experience via the comment section below.
Want to join a great team? Check out our careers section. We are always looking for outstanding talent—from application specialist to software developers.
📷 Photo credits: daniela-mueller.com