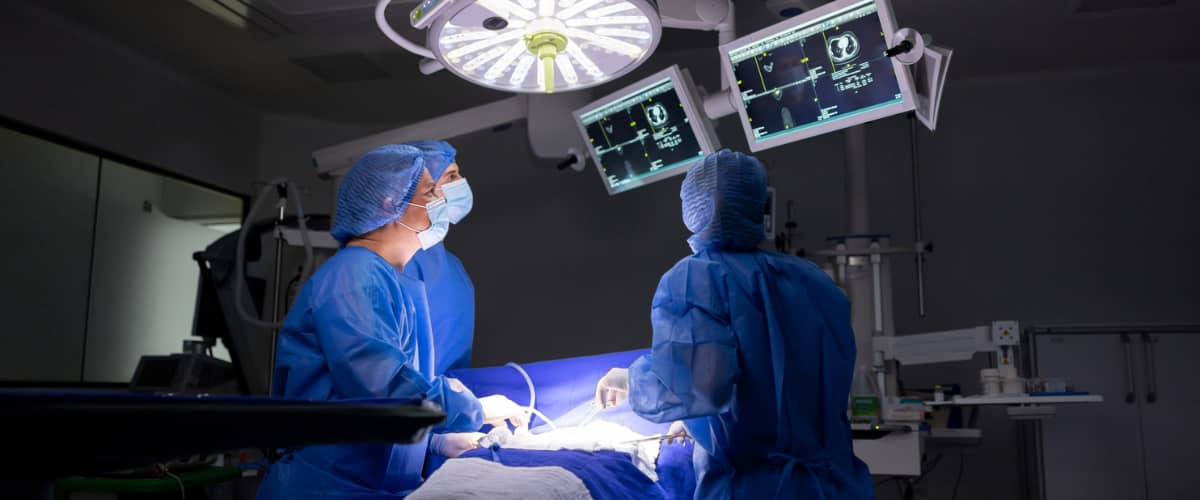
There are three main types of radiology: diagnostic radiology, interventional radiology, and radiation therapy. Let’s explore them in more detail.
📖 Author: Emmanuel Anyanwu | Alberta Health Services, Canada
Radiology is a dynamic and indispensable branch of medicine that utilises advanced imaging techniques to visualise inside of the human body. It plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of various medical conditions.
Radiological techniques have evolved significantly over the years, leading to the emergence of various specialised fields within radiology, each tailored to address specific medical concerns. There are three types of radiology: diagnostic radiology, interventional radiology, and radiation therapy.
Types of radiology: Diagnostic radiology
Diagnostic radiology is the cornerstone of medical imaging. It encompasses a wide range of imaging modalities that create detailed visual representations of the interior of the human body.
These images are essential for diagnosing, monitoring, and guiding the treatment of a wide range of medical conditions. It is an essential component of modern healthcare to provide invaluable insights into the human body’s inner workings.
It enables early diagnosis, precise treatment planning, and ongoing monitoring of medical conditions, ultimately contributing to improved patient care and outcomes. Some examples of diagnostic radiology include X-ray, CT, mammography, PET.
Diagnostic radiology modalities
Diagnostic radiology encompasses a variety of imaging modalities, each suited for different purposes and anatomical areas:
- X-ray Radiography: X-rays are directed through the body onto a detector, creating 2D images, commonly used for skeletal imaging, detecting fractures, and assessing lung conditions.
- Computed Tomography (CT): CT scans combine X-rays with computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images, making it valuable for visualising soft tissues, detecting tumours, and trauma assessment.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures, particularly useful for brain and spinal cord imaging, joint assessments, and soft tissue evaluations.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images. It is widely used for monitoring fetal development during pregnancy, assessing abdominal organs, and guiding minimally invasive procedures.
- Nuclear Medicine: Nuclear medicine involves the use of radioactive tracers to visualise and assess organ function and metabolic processes, especially useful for cancer staging and assessing cardiac function.
- Fluoroscopy: Fluoroscopy provides real-time moving images, commonly used to assess digestive and urinary systems, and female reproductive organs.
Significance in medicine
Diagnostic radiology is of paramount importance in medicine for several reasons:
- Early diagnosis: It allows for the early detection of diseases and conditions, enabling timely intervention and treatment.
- Treatment planning: Radiological images aid in planning surgical procedures and guiding minimally invasive interventions, improving the precision of medical treatments.
- Monitoring: Radiology plays a crucial role in monitoring disease progression and treatment efficacy over time.
- Non-invasiveness: Many diagnostic radiology procedures are non-invasive, reducing the need for exploratory surgeries and minimising patient discomfort.
- Research & education: Radiological images are invaluable for medical research and education, facilitating the training of healthcare professionals and advancing medical knowledge.
Types of radiology: Interventional radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a dynamic and rapidly evolving subspecialty of radiology that combines imaging techniques with minimally invasive procedures to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions.
Interventional radiologists use real-time imaging guidance to access and treat specific areas of the body, often avoiding the need for traditional surgery.
Some examples of interventional radiology include needle biopsy, feeding tube placement, embolisation, breast biopsy, venous access catheter placement, like ports and PICCs, vertebroplasty, and kyphoplasty.
Interventional radiology operates on several fundamental principles such as a minimally invasive approach, real-time imaging, and precision.
Applications of interventional radiology
Interventional radiology has a wide range of applications across various medical specialties, including:
- Vascular interventions: This involves the diagnosis and treatment of vascular conditions, such as arterial blockages, aneurysms, and venous thrombosis. Procedures include angioplasty, stent placement, and thrombolysis.
- Oncology: Interventional radiologists play a crucial role in cancer care, performing procedures like tumour embolisation, radiofrequency ablation, and chemo-embolisation to shrink or treat tumours.
- Gastrointestinal & hepatobiliary interventions: IR is used for procedures like percutaneous biliary drainage, gastrostomy tube placement, and liver biopsy.
- Urology: Interventional radiology is employed for procedures like nephrostomy tube insertion, ureteral stent placement, and percutaneous stone removal.
- Musculoskeletal interventions: IR can treat conditions like bone fractures, joint infections, and musculoskeletal pain through procedures such as bone biopsies and joint injections.
- Pain management: It is used for the management of chronic pain conditions through procedures like nerve blocks and epidural injections.
- Women’s health: IR can address conditions like uterine fibroids and pelvic congestion syndrome through uterine artery embolisation and ovarian vein embolisation.
Significance in modern medicine
Interventional radiology offers several significant advantages in modern medicine:
- Minimally invasive: IR procedures are less invasive than traditional surgery, resulting in smaller incisions, reduced pain, and quicker recovery times for patients.
- Targeted treatment: Interventional radiology allows for precise targeting of specific areas, minimising collateral damage to healthy tissues.
- Alternative to surgery: Many conditions that once required open surgery can now be treated with IR techniques, reducing risks and complications.
- Reduced hospital stay: Patients undergoing IR procedures often experience shorter hospital stays or may even be treated on an outpatient basis.
- Versatility: IR techniques can be applied to a wide range of medical conditions across multiple specialties, making it a versatile and adaptable field.
Types of radiology: Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy, often referred to as radiotherapy, is a crucial and highly specialised medical treatment that employs targeted doses of ionising radiation to treat and manage various diseases, most notably cancer.
This therapy is a cornerstone in the fight against cancer and plays a pivotal role in either curing or controlling the growth of malignant tumours.
Significance in modern medicine
Radiation therapy plays a vital role in modern medicine for several reasons:
- Cancer treatment: Radiation therapy is a critical component in the treatment of various cancers, either as a primary treatment or in combination with surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. It can achieve tumour shrinkage, control tumour growth, or eradicate cancer cells altogether.
- Palliative care: Radiation therapy is used to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for cancer patients, particularly in cases where a cure is not possible. It can help manage pain, bleeding, and other distressing symptoms.
- Preservation of organ function: In some cases, radiation therapy can be used to shrink tumours before surgery, making it possible to remove less tissue and preserve organ function.
- Local control: Radiation therapy is highly effective in achieving local control of cancer, particularly when tumours are confined to a specific area.
- Advancements: Ongoing research and technological advancements have led to more precise and targeted radiation therapy, minimising side effects, and improving patient outcomes.
The diverse array of types of radiology represents a collective triumph of medical science and technology, offering an indispensable toolkit for healthcare professionals in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of a vast range of medical conditions.
From the foundational diagnostic radiology that provides insights into anatomical structures to the precision of interventional radiology that minimises invasiveness, and to the life-saving capabilities of radiation therapy, all types of radiology serve as a vital component of modern medicine.
As technology continues to evolve and our understanding of medical imaging deepens, the potential for further advancements in radiology is limitless.
These advancements promise to further enhance patient care, improve treatment outcomes, and expand our capacity to explore the intricacies of the human body, ultimately fostering a healthier future for all.
—
Are you using any of these types of radiology? Share your experience via the comment section below.
Want to join a great team? Check out our careers section. We are always looking for outstanding talent—from application specialist to software developers.
📷 Photo credits: daniela-mueller.com