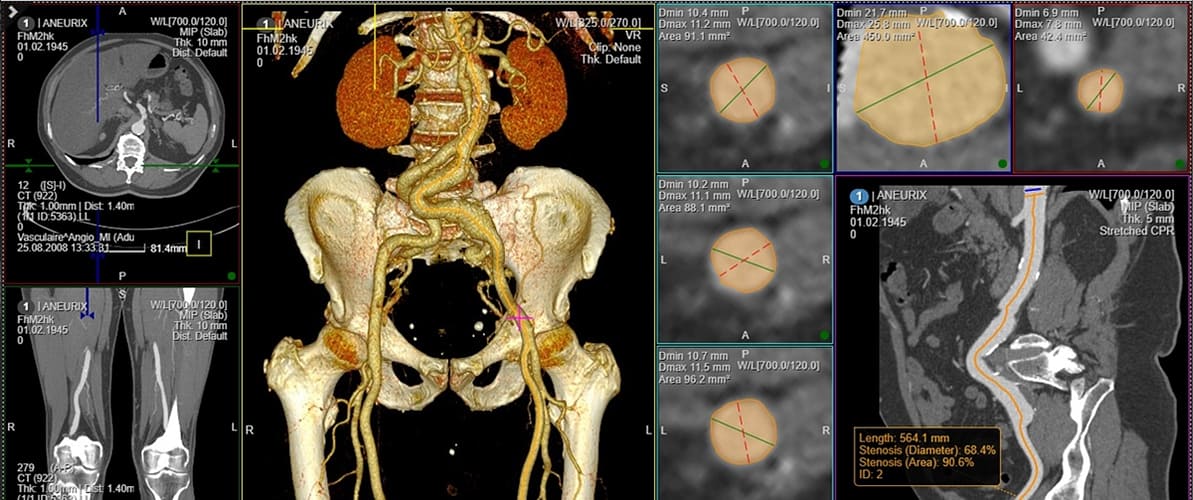
360-degree viewing in radiology uses advanced technology to comprehensively visualise medical imaging data—improving diagnostic accuracy and transforming how medical professionals interact with data for better healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
📖 Author: Emmanuel Anyanwu | Alberta Health Services, Canada
360-degree viewing technology in radiology refers to a comprehensive approach to viewing medical imaging data in a three-dimensional, all-encompassing manner.
It involves utilising advanced technologies and tools to visualise medical images from every angle—allowing healthcare professionals to explore and analyse the data thoroughly.
This approach enhances diagnostic accuracy, facilitates detailed analysis, and provides a holistic view of the patient’s condition. 360-degree viewing technology revolutionises the way medical professionals interact with imaging data.
By providing a comprehensive and interactive view, it enhances diagnostics, surgical planning, medical training, and patient education, ultimately improving the quality of healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
360-degree viewing: fields & applications
- Diagnostic radiology: In diagnostic radiology, 360-degree viewing enables radiologists to examine medical images, such as CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays, from various angles. This detailed visualisation aids in detecting abnormalities, tumours, fractures, and other medical conditions with higher precision.
- Surgical planning: Surgeons use 360-degree viewing technology to plan complex surgical procedures. By visualising a patient’s anatomy in three dimensions, surgeons can create detailed pre-operative plans, improving the accuracy of surgeries and minimising risks.
- Interventional radiology: Interventional radiologists utilise 360-degree viewing to guide minimally invasive procedures, such as catheter insertions and biopsies. Their technology provides real-time imaging, enhancing the precision and safety of these interventions.
- Education & training: Medical students and healthcare professionals can learn about human anatomy and various medical conditions using 360-degree viewing technology. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications allow immersive learning experiences, aiding in medical education.
- Patient education: 360-degree viewing applications can be used to educate patients about their conditions. Visualising their own medical images in an interactive 3D format helps patients understand their diagnoses and treatment plans much better.
- Rehabilitation & therapy: 360-degree viewing applications are employed in rehabilitation and therapy programs. Patients recovering from injuries or surgeries can engage in immersive exercises and therapy sessions—enhancing their rehabilitation experience and improving outcomes.
Technological aspects
- Virtual reality (VR) & augmented reality (AR): VR and AR technologies provide immersive 360-degree viewing experiences. VR headsets and AR applications allow users to interact with medical images in a virtual environment, enhancing visualisation and understanding.
- 3D reconstruction: Advanced software tools process medical data and reconstruct 2D medical images into interactive and detailed 3D models or visualisations. These models can be rotated, zoomed, and explored from various angles—providing a comprehensive view of the patient’s anatomy. Thus, enabling healthcare professionals to explore patient data, medical images, and anatomical models in a comprehensive manner, aiding in diagnostics and treatment planning.
- PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems): PACS systems enable the storage, retrieval, and interpretation of medical images. Integration with 360-degree viewing technology enhances the capabilities of PACS—allowing for in-depth analysis and collaborative decision-making.
- Holographic imaging: Holographic displays create 3D holograms of medical images, enabling users to view and interact with the images in a 360° manner. This technology offers a realistic and immersive experience for medical professionals.
- 360° cameras & sensors: Specialised cameras and sensors capture 360° images and videos of medical environments. This technology is valuable for remote consultations, medical training, and creating virtual walkthroughs of healthcare facilities.
In summary, 360-degree viewing in radiology harnesses advanced technologies like VR, AR, and 3D reconstruction to provide a comprehensive understanding of medical images, including immersive and detailed perspectives of medical data and environments.
From diagnostics and surgery planning to patient education and medical training, 360-degree viewing enhances healthcare outcomes and experiences for both healthcare professionals and patients.
—
Do you love using 360-degree viewing tools? Share your experience via the comment section below.
Want to join a great team? Check out our careers section. We are always looking for outstanding talent—from application specialist to software developers.
📷 Photo credits: daniela-mueller.com